We all like a good holiday by the beach. But how often have you wondered why beaches are as they are? Why does a beach change its form on an almost daily basis? Why are there massive rocks piled up at the bottom of the cliffs and why are there strange wooden fences projecting out into the sea. This unit will provide the focus for the coursework at IST in 2023 and and will change your view of the coastline forever. You will never be able to go to the beach again, without noticing all the things you are about to learn about. Sorry!
There is one case study here which will be your Sitges coursework (2022 & 2023) to cover the opportunities (tourism) & management (coastal defences).
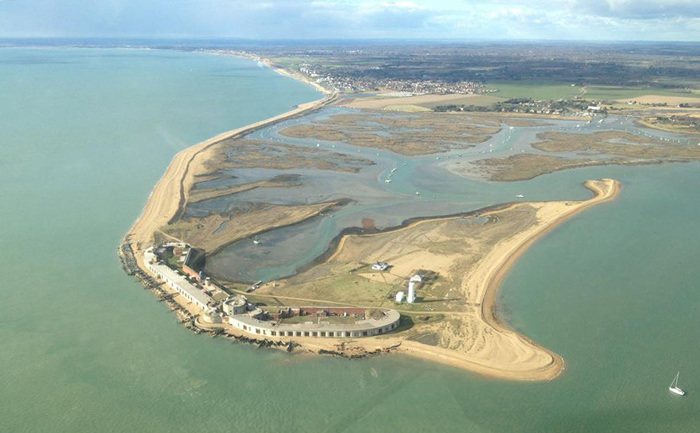
Coastlines - Why Are They Important?
Starter: Using the images above and your own knowledge, explain how coasts are used and why they are important. You can record your thoughts on the worksheet beneath
| Importance of Coasts | |
| File Size: | 2146 kb |
| File Type: | docx |
Using the three images above and your own knowledge, explain why coastlines around the world are under threat. Again, record your thoughts on the worksheet.
Ocean Waves - How Do They Work?
|
Objective: To find out how waves are created.
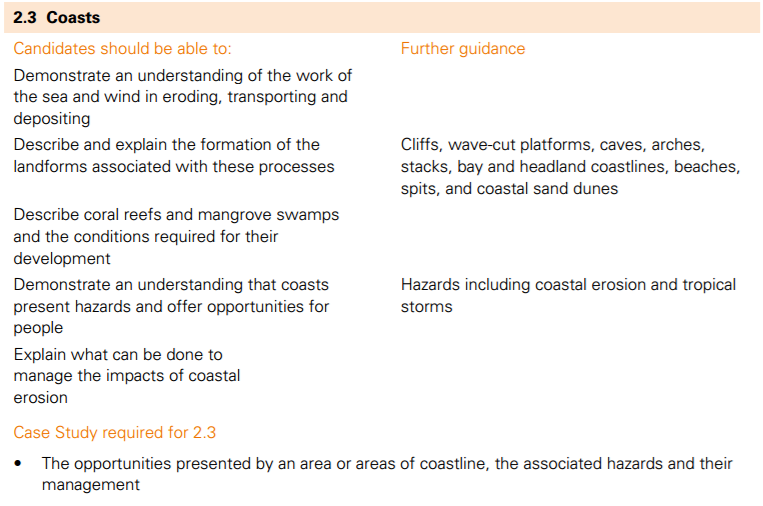
The coast is the name given to the zone where the land meets the sea/ocean. Coasts are shaped by the sea and the action of waves. The processes that take place are erosion, transportation and deposition. The action of waves The power of waves is one of the most significant forces of coastal change. *Waves are created by wind blowing over the surface of the sea. *As the wind blows over the sea, friction is created - producing a swell in the water. *The energy of the wind causes water particles to rotate inside the swell and this moves the wave forward. The size and energy of a wave is influenced by:
Task 1 - Click on the diagram to the right hand side to enlarge. Make a sketch of this in your workbook and label accordingly. Add an arrow to represent fetch too. Task 2 - Now watch the first 2.15 of the YouTube video above to reinforce what you have just learnt. Task 3 - Mix & Match Match the correct keyword to definition from the list underneath. Use your highlighter pen on each key word as they are really important for your exam. |
|
|
Crest:
Backwash: Velocity: Wavelength: Trough: Wave height: Swash: Wave Frequency: |
The top of the wave.
The low area in between two waves. The distance between two crests or two troughs. The distance between the crest and the trough. The number of waves per minute. The speed that a wave is traveling. It is influenced by the wind, fetch and depth of water. The movement of water and load up the beach. The movement of water and load back down the beach. |
The Movement & Types Of Ocean Waves
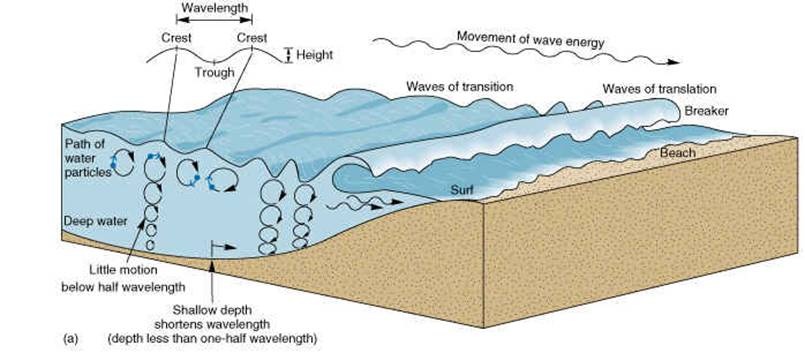
Swash & backwash - Watch the video, study the diagram and then check out this revision page.
Task 1 - Using your worksheet, explain how the process works and draw a diagram.
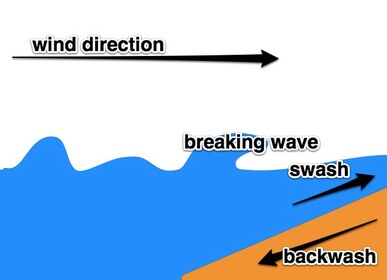
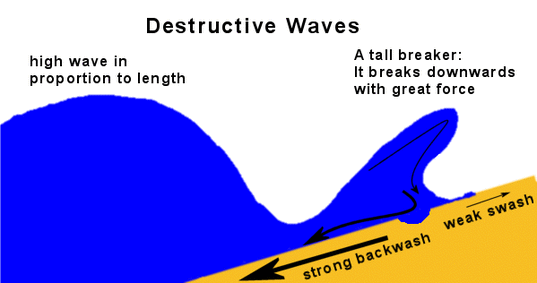
Task 2 - There are two types of waves, constructive and destructive (deconstructive).
i. Watch the two YouTube videos below and then study the diagrams next to them.
ii. Then TURN YOUR VOLUME DOWN and click here (Enable Flash) to be taken to an interactive resource where you can examine both.
If that doesn't work, check out this page from the BBC.
On your worksheet, make notes on destructive & constructive waves (there are four stages for the notes to match the interactive graphic above) and create a sketch diagram to show the features of each types of wave.
Task 3 - Please add the following two sentences to your diagrams and notes;
1. Constructive waves build. They create beaches and happen when swash is stronger than backwash. Beaches that experience constructive waves can be quite flat.
2. Destructive (deconstructive) waves erode. Backwash is stronger than swash. They are a major cause of erosion and on beaches, they remove beach material and wash it out to sea. Beaches that experience destructive waves can be quite steep.
Task 1 - Using your worksheet, explain how the process works and draw a diagram.
Task 2 - There are two types of waves, constructive and destructive (deconstructive).
i. Watch the two YouTube videos below and then study the diagrams next to them.
ii. Then TURN YOUR VOLUME DOWN and click here (Enable Flash) to be taken to an interactive resource where you can examine both.
If that doesn't work, check out this page from the BBC.
On your worksheet, make notes on destructive & constructive waves (there are four stages for the notes to match the interactive graphic above) and create a sketch diagram to show the features of each types of wave.
Task 3 - Please add the following two sentences to your diagrams and notes;
1. Constructive waves build. They create beaches and happen when swash is stronger than backwash. Beaches that experience constructive waves can be quite flat.
2. Destructive (deconstructive) waves erode. Backwash is stronger than swash. They are a major cause of erosion and on beaches, they remove beach material and wash it out to sea. Beaches that experience destructive waves can be quite steep.
How Do Ocean Waves Erode?
|
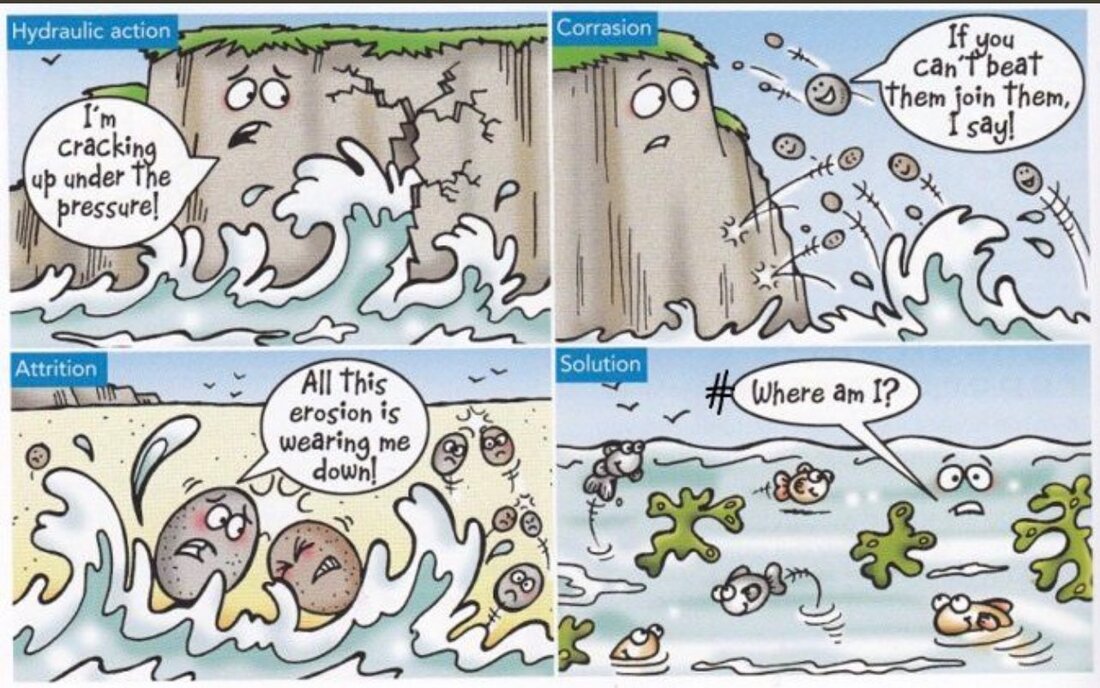
Task 1 - Watch the cliff collapse video in Cornwall, UK, to the right. This happens all the time around the world - the sea wins! It's not always caught on camera though. This has happened as a result of a number of erosional processes. We are going to learn about these next. Task 2 - Complete the worksheet above by using the information in this section. Coastal Erosion (types of erosion) Coasts being at the boundary of the land and the sea are extremely vulnerable to erosion. They are attacked by the immense power of the sea and the weather. The main ways that the sea erodes the coast are: Hydraulic Pressure: This is when sea water and air get trapped in cracks. The increasing pressure of the water and air cause the rocks to crack. Corrasion (abrasion): Rocks been thrown into the cliffs by waves and breaking off bits of the cliff. Corrosion (solution): The slight acidity of sea water causing bits of the cliff to dissolve. Attrition: Rocks, sand and stones being thrown into each other by the sea current and waves. Task 3- Watch the IGCSE video hosted by someone familiar (to the right). What type of erosion can you see evidence of? Take a screen shot of part of the video, crop and annotate with key features. How would this look in an examination? - Check out this video. |
|
What Are The Features Of Erosion?
Part 1 - Bays & Headlands
|
Objective: To discover how erosion causes different coastal features.
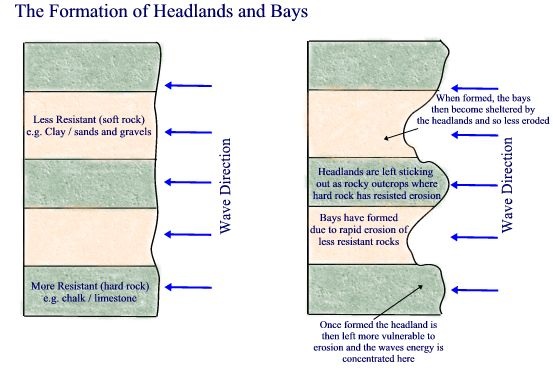
Bays and Headlands Bays and headlands are formed in a very similar way to rapids (rivers topic). They are formed when you get alternate layers of hard and soft rock. The sea is able to erode the soft rock a lot quicker than the hard rock making a bay. The harder rock forms a headland. Bay An indented area of land normally found between two headlands. Bays are usually more sheltered so there is less erosive power, meaning you often find beaches in bays. Headland A piece of land that sticks out into the sea. Waves refract around headlands so they experience a lot of erosion forming features like arches and stacks (see below). Task 1 - Watch the video above from 2:20 to 4:35. This shows the process of headland and bay formation. Task 2 - Use the worksheet below to explain the process of bay and headland formation . |
|
Part 2 - Caves, Arches, Stacks & Stumps
|
Caves, Arches, Stacks and Stumps
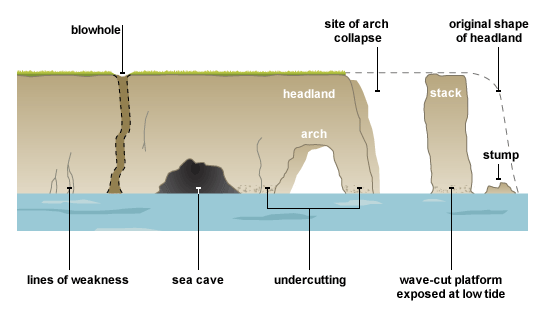
Step 1 - Check out this excellent video from Time for Geography. Caves, arches, stacks and stumps are usually found on headlands, where wave refraction is causing erosion on three sides. The waves always look for weaknesses in the headland (cracks and joints). If they find a crack or a joint they will start attacking it. Hydraulic pressure will be the main type of erosion. Overtime the crack may turn into a cave. Slowly the cave will get bigger and cut all the way through the headland, making an arch. As the arch gets bigger the weight of the arch roof gets too great and it collapses, leaving a stack. The stack is then eroded by the sea and weathered from the air leaving a stump. Blowhole: Sometimes the sea may erode through to the top of the headland (following a large crack). If this happens a blowhole is created. Watch the really excellent video to the right hand side. Who would have thought that we could use plasticine to show the process!! Anyone fancy trying this out at home in their sandpit? Task - Use the worksheet to the right to create an annotated sketch using the diagrams, YouTube video and description above to explain how caves, arches, stacks & stumps form. Don't forget to add a blowhole too. |
How would this look in the examination? - Check out this video. You can pause the video and have a go at answering. |
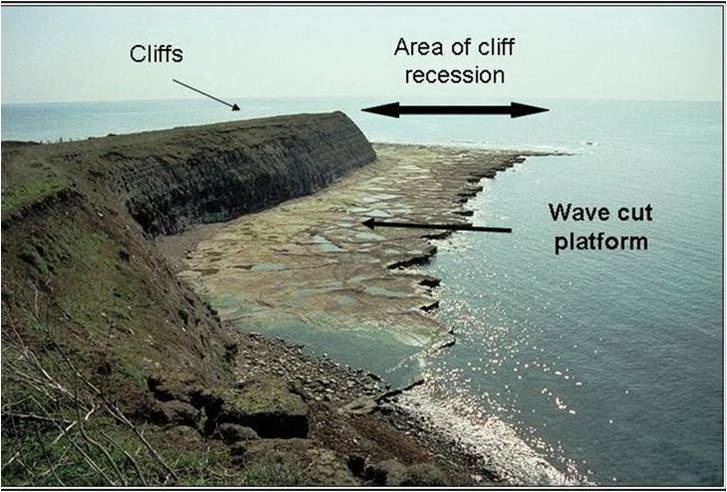
Part 3 - Wave Cut Platforms
|
Wave cut platforms are made in a similar ways to waterfalls and gorges (rivers topic). At high tide the power of the sea attacks and erodes the bottom of the cliff.
Over time this erosion creates a wave cut notch (basically an eroded hole at the bottom of the cliff). As the wave cut notch gets bigger, the weight of rock above the notch gets greater. Eventually the cliff can not support its own weight and it collapses. The process then starts again, with the erosion of the sea making a new wave cut notch. As the process continues the cliff starts to move backwards (retreat). Because the cliff is moving backwards a wave cut platform (an expanse of bare rock) is created. Wave cut platforms are only visible at low tide. Task i. Watch the first video to the right (amateur!) and this one (professional). ii. Make a sketch of the image above onto the worksheet. iii. Annotate all the main features using the description above and information from the videos. iv. Add some colour to bring the diagram to life. How would this look in an examination? - Complete the exam question on the second side of the worksheet. Once complete, Check out this video. How did you do? |
|
Process of Transportation - Longshore Drift
|
Objective: To find out how waves move material many KM along the coastline.
Longshore Drift or LSD is an important process on every beach. It is the process by which material moves along the beach everyday. If you painted a pebble bright pink, left it and came back one week later, the sea would have moved it to a completely different part of the beach. Spend 5 minutes watching Mr Rogers (a very good Geography teacher from Portsmouth, UK) explaining how Longshore Drift works. Task 1- Design your own diagram to show how LSD works based on what Mr Rogers says and draws. Annotate it with as much detail as possible. |
Groynes: Groynes are wooden or concrete fences (walls) placed out into the sea to stop longshore drift happening.
**IST Students - You will see these in Sitges! |
The Features of Deposition
|
Objective: To recognise and explain the formation of the features deposited by the sea
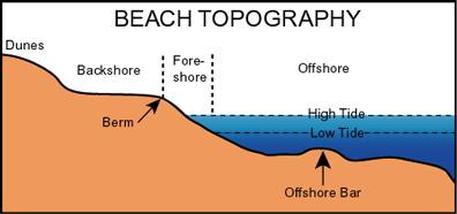
Beach: The beach is the accumulation of sand between the lowest spring tides and the highest spring tides. Beaches can be made out of sand, shingle and/or pebbles. Beaches receive their material from longshore drift, constructive waves, cliff erosion and river discharge. Beaches cane be divided into backshore, offshore and foreshore. The backshore is the area above the normal high tide level, the foreshore is the area in between normal high and low tide and offshore is the area below the normal low tide. Berm: The berm is a ridge (long thin hill) that forms at the top of the beach. It is the highest section of the beach and is basically sand accumulated on the strand line (twigs, litter, seaweed, etc. deposited at high tide). Intertidal zone: The area of land between high tide and low tide. Strand line: The material (seaweed, driftwood) that is deposited by the sea at furthest point of the high tide. Task - Complete the worksheet above.
|
Spit - A Feature of Transport & Deposition
|
Objective: To complete a mini study on the processes that result in the formation of a coastal spit and its features.
Task 1 - Watch the two minute explanation video on the YouTube video to the right. Task 2 - Complete the worksheet below (by hand if possible) labeling the coastal processes leading to the formation of Hurst Spit (UK) as well as its physical features using information from the video task. If you want to see what a spit is like to walk on, check out the embedded Google Street View at the bottom of this section. Task 3 - How might this look in the examination? - Complete the exam question by downloading the worksheet below. |
|
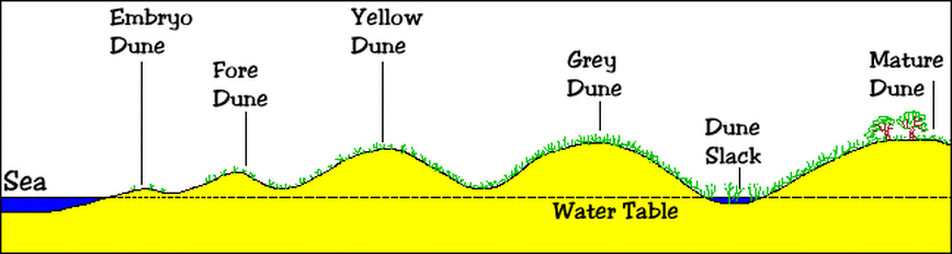
How Do Sand Dunes Form?
Objective: To find out how sand dunes are formed.
Starter: Watch the first three minutes of this video, from Time for Geography (note the subtitle language options).
Task - Using the rest of the Time For Geography video and the PowerPoint presentation below, complete the tasks on the worksheet above.
PowerPoint (source: https://geographylhs.wikispaces.com)
Alternative Task
Click here to access your sand dunes worksheet. Complete all tasks set out using all information within.
Thanks to: http://www.sussex.ac.uk/geography/researchprojects/BAR/worksheets.html
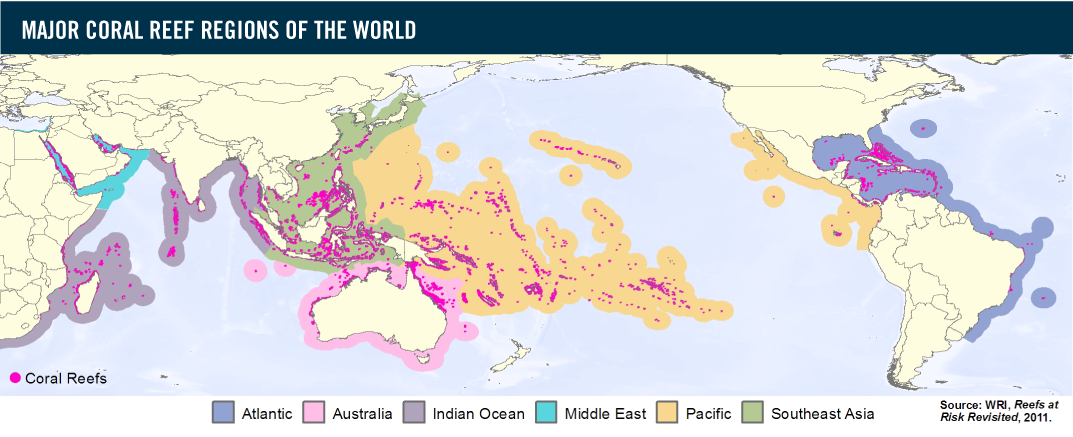
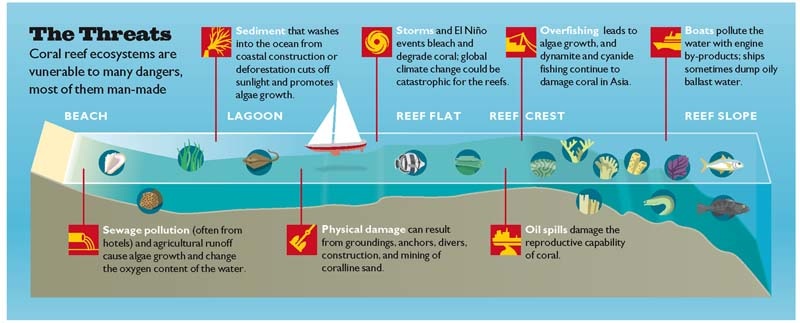
How Do Coral Reefs Form?
Objective: To discover where and how coral reefs form and the threats posed to them by human activity.
Starter: Take a Google 'reefview' tour around Batu Bolong (check out on Google Maps if you've never heard of it before!). If you've never been reef diving before, this is what it looks like. Impressive or what!?
Coral reefs are large underwater structures composed of the skeletons of coral, which are marine invertebrate animals. The coral species that build coral reefs are known as hermatypic or"hard" corals because they extract calcium carbonate from seawater to create a hard, durable exoskeleton that protects their soft, sac-like bodies.
Each individual coral is referred to as a polyp. New coral polyps live on the calcium carbonate exoskeletons of their ancestors, adding their own exoskeleton to the existing coral structure. As the centuries pass, the coral reef slowly grows, one tiny exoskeleton at a time, until they become massive features of the submarine environment. - source: livescience.com
Starter: Take a Google 'reefview' tour around Batu Bolong (check out on Google Maps if you've never heard of it before!). If you've never been reef diving before, this is what it looks like. Impressive or what!?
Coral reefs are large underwater structures composed of the skeletons of coral, which are marine invertebrate animals. The coral species that build coral reefs are known as hermatypic or"hard" corals because they extract calcium carbonate from seawater to create a hard, durable exoskeleton that protects their soft, sac-like bodies.
Each individual coral is referred to as a polyp. New coral polyps live on the calcium carbonate exoskeletons of their ancestors, adding their own exoskeleton to the existing coral structure. As the centuries pass, the coral reef slowly grows, one tiny exoskeleton at a time, until they become massive features of the submarine environment. - source: livescience.com
Task - Using the worksheet above and the evidence board below, complete all tasks set out on the worksheet.
Coral Reef Evidence Board - Use to complete worksheet
|
Help Video |
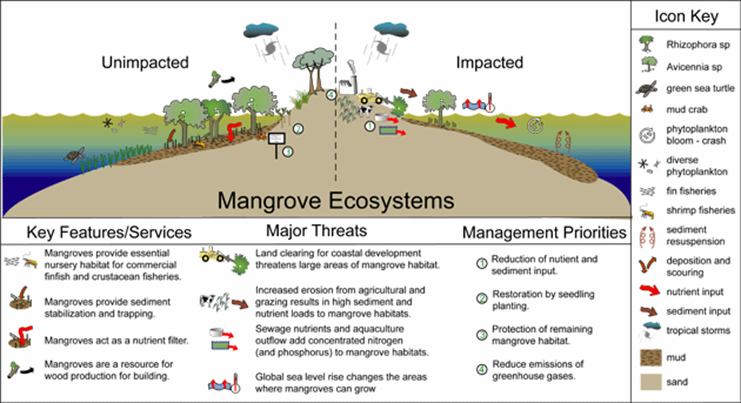
Why Are Mangrove Swamps Important?
|
|
|
Task 1 - Read this September 2016 article on the importance of Mangroves as a natural resource and also as flood protection and complete the following tasks. Create your own worksheet that includes the image below. Then complete the following questions using the article above and the second video (above):
1. What are mangroves and where do they naturally grow?
2. Explain what 'the roots also act as buffers' mean in terms of protection from flooding and tsunami's
3. What 'death rate comparison' can be made over their effectiveness after the 2004 Asian Tsunami?
4. Outline what is being done to resolve the problem caused by mangrove removal.
5. How is the removal of mangroves also linked to coastal erosion?
Task 2 - Watch the short video beneath and study the image below. Make notes on further values and threats that you see on the video.
Optional Task
Stop Start Animation Task
|
Objective: To create an RSA style video using a technique of your choice to show coastal processes (erosional & depositional).
RSA videos are those that are manipulated by speeding up, slowing down, time lapse and over dubbed with your voice. You might remember seeing some examples produced by Year 11 students at the International School of Toulouse and Priory School, Portsmouth to the right. These are examples of sped up videos that are over dubbed with narrative showing the changes to the river features on the River Garonne. They are brilliant ways of learning and remembering geographical processes. Your task is to complete an RSA style video that incorporates the following: 1. Erosion of headlands (joint, crack, cave, arch, stack, stump) 2. Transportation - LSD 3. Deposition - Beaches and/or spits. You can do a traditional RSA like the first two videos or something a little more creative like the video to the right with Plasticine. There is another video above (Headland Erosion by Jasmine) that is more iGCSE in style. Your efforts will be presented to the rest of the world on YouTube and a winner chosen. |
|
|
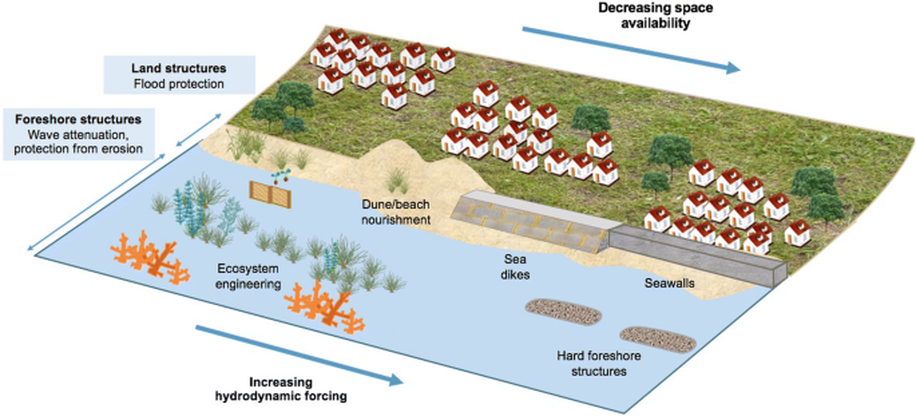
Objective: To find out how humans try to win the fight with the sea and its erosive power.
Starter: Watch the 'Eliot legend' video to the right, from 10 minutes onward. When it comes to protecting the coastline, a mixture of both hard and soft engineering approaches are used to preventing coastal erosion and transportation. These protection methods are often present in areas where tourism / settlement has been developed. Go back and find your favourite beach, and see if you can see any evidence of coastal protection happening. Check out the diagram above for more info. Hard Engineering may be defined as: A technique involving the construction of significant man-made structures to manage the coastline. e.g. Sea walls and rock armour Soft Engineering may be defined as: A technique involving the construction of more environmentally friendly, less damaging and arguably more sustainable management solutions. e.g. beach nourishment or managed retreat Task - Put together your own fact sheet that aims to show the different ways that coasts can be protected from destructive waves, how those defenses work and their pros and cons. There is a help sheet below right... Part 1 - Hard engineering approaches - Time for Geography Video link here (groynes, sea wall, gabions etc) Part 2 - Soft engineering approaches - Time for Geography Video link here. |
|
Case Study - Sitges, Spain.
You will need an example of coastal erosion management for Paper 1 . In the years where we go to Spain for our fieldwork, your coursework will be used to cover this section of work. In other years, you will need to download the fact sheet below and use for revision purposes.