Pressure on resources & the future security of places.
Objective: to gain and understanding of the complexities of 'The Nexus' and how its complex interactions affect:
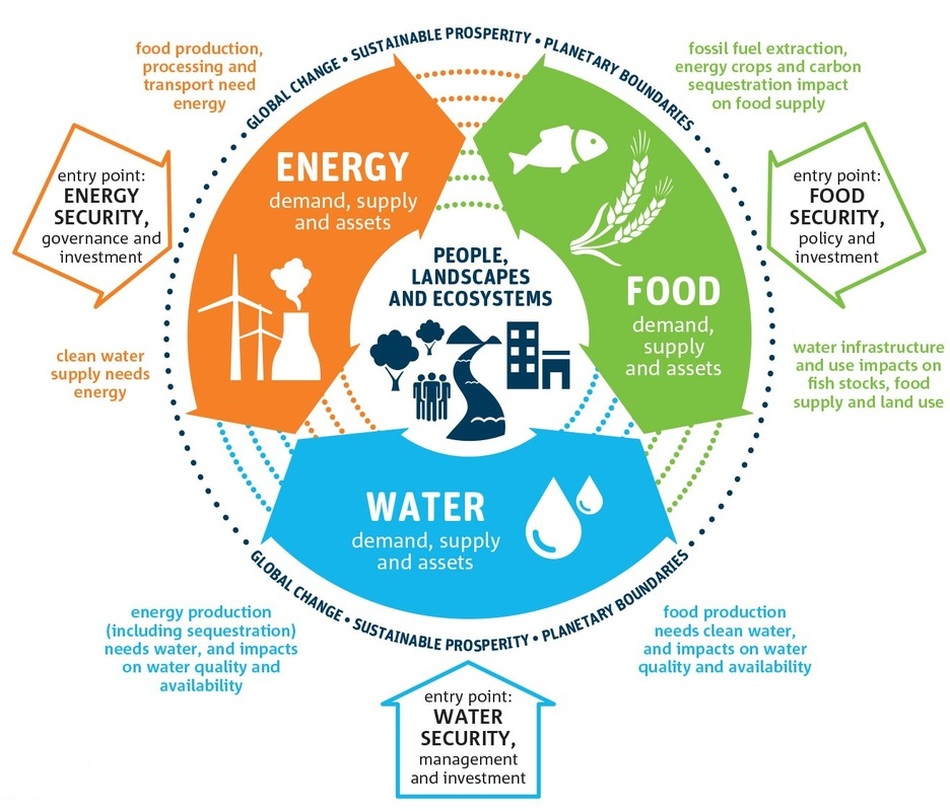
• national water security, including access to safe water
• national food security, including food availability
• national energy security, including energy pathways and geopolitical issues
• national water security, including access to safe water
• national food security, including food availability
• national energy security, including energy pathways and geopolitical issues
"Trade-offs between energy and water, or between energy and food, are increasingly being debated in terms of the 'nexus' – a buzzword which has risen in prominence over the past few years as a way of thinking about interconnections between food, water, energy and the environment. These systems are inextricably linked, and integrated approaches are required, which move beyond sectoral, policy and disciplinary silos"
James Wilsdon and Rose Cairns June 2014
James Wilsdon and Rose Cairns June 2014
Note students should not be directed to this page before undertaking the following activity.
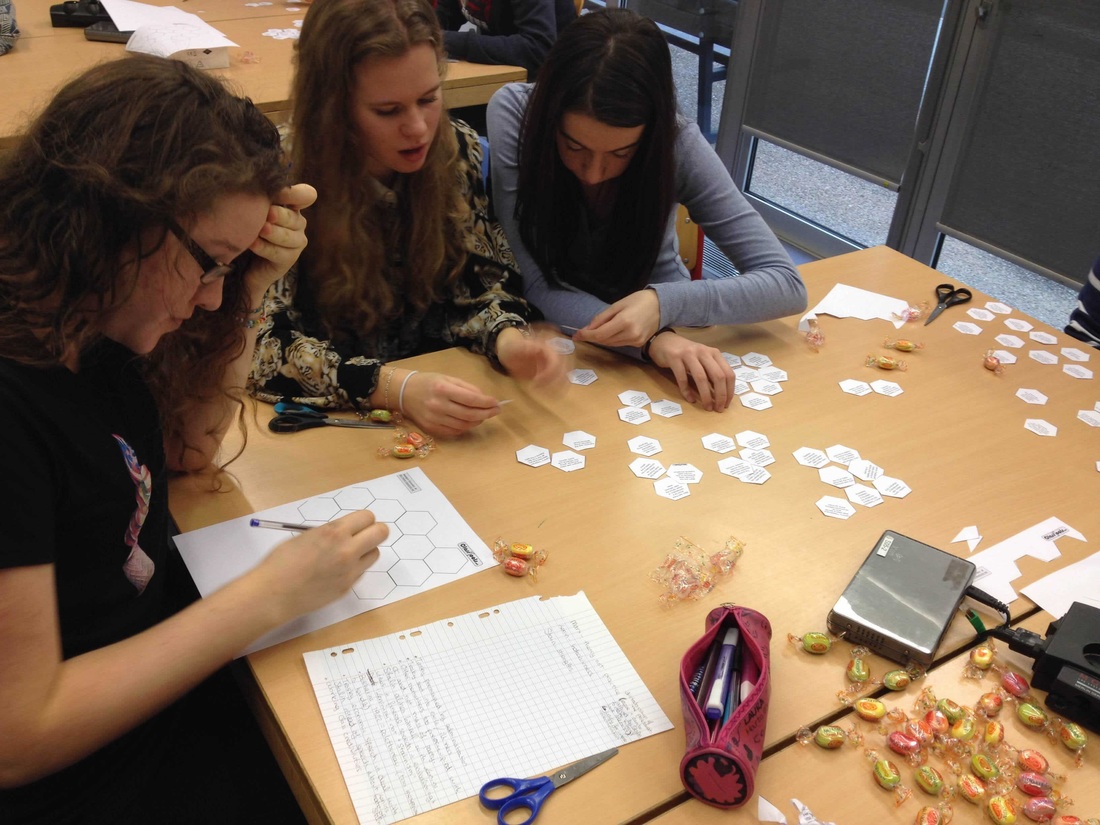
Task - We are going to use solo hexagons to critically examine the complexities between the Nexus of water, food, energy and climate change. To to this the following resources are important.
Task - We are going to use solo hexagons to critically examine the complexities between the Nexus of water, food, energy and climate change. To to this the following resources are important.
|
Step 1 - The Preparation
Split your teaching group into pairs or groups of three. Explain to the students that they are going to be completing a hexagon activity and that there is no right or wrong answer. The key thing is the discussion that goes with the activity and making as many links between as many global issues as possible. Step 2 - The Traditional Approach
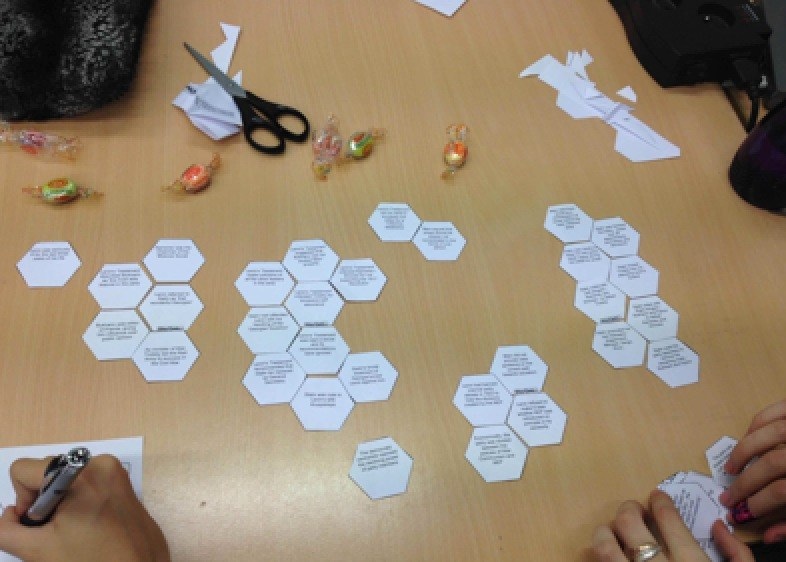
Step 3 - The Nexus Approach & Critical Thinking
|
Step 4 - The final display
Step 5 - Links with the SDG's
Step 6 - Exam Corner
- The students would then be given time to organize their cards (paper versions) onto display card.
Step 5 - Links with the SDG's
- A plenary would include a final pack of hexagons each with the logo of the 17 SDG’s where students have to fit them into the diagram as extensions to the hubs and nodes that they already have glued down.
Step 6 - Exam Corner
- The sequence of the hexagons diagram could then be further examined by using a hexagons Venn Diagram and ultimately used in conjunction with the IB essay planner to formulate a response to the following 15 mark homework question
“Water, food and energy security can no longer be viewed as isolated global problems” – critically examine this statement (15)
Additional Resources - For follow up lessons (not yet planned)
|
|
|
Sources of information.
With thanks to Russel Tarr for his ideas and inspiration.
http://www.classtools.net/blog/venn-diagrams-compare-and-contrast-two-three-factors-visually/
http://www.classtools.net/blog/using-hexagon-learning-for-categorisation-linkage-and-prioritisation/
http://www.classtools.net/hexagon/
With thanks to Russel Tarr for his ideas and inspiration.
http://www.classtools.net/blog/venn-diagrams-compare-and-contrast-two-three-factors-visually/
http://www.classtools.net/blog/using-hexagon-learning-for-categorisation-linkage-and-prioritisation/
http://www.classtools.net/hexagon/