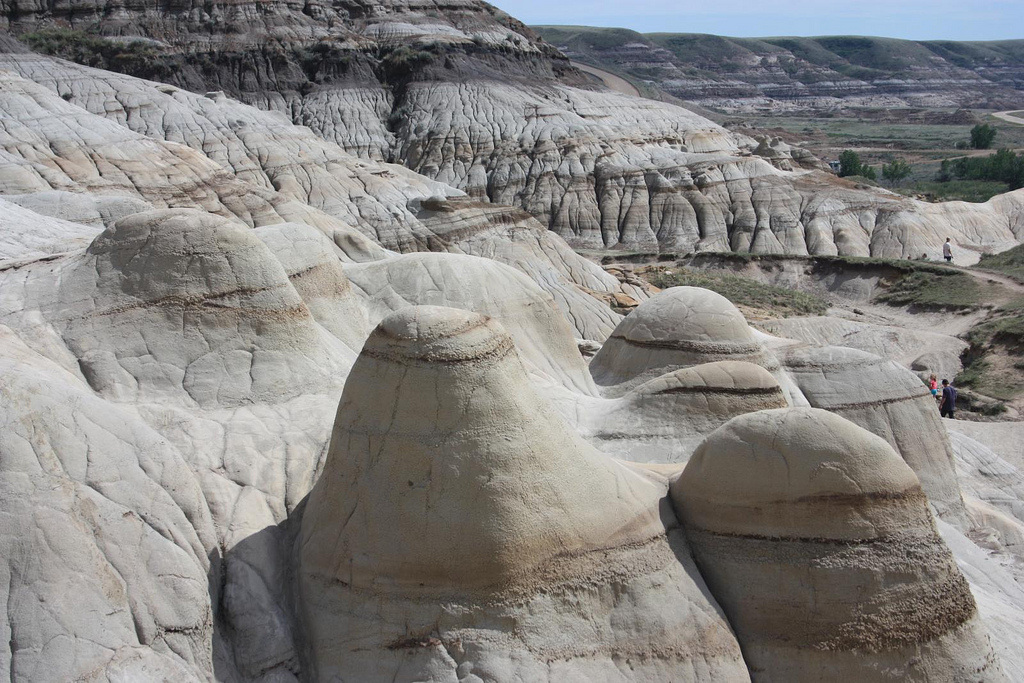
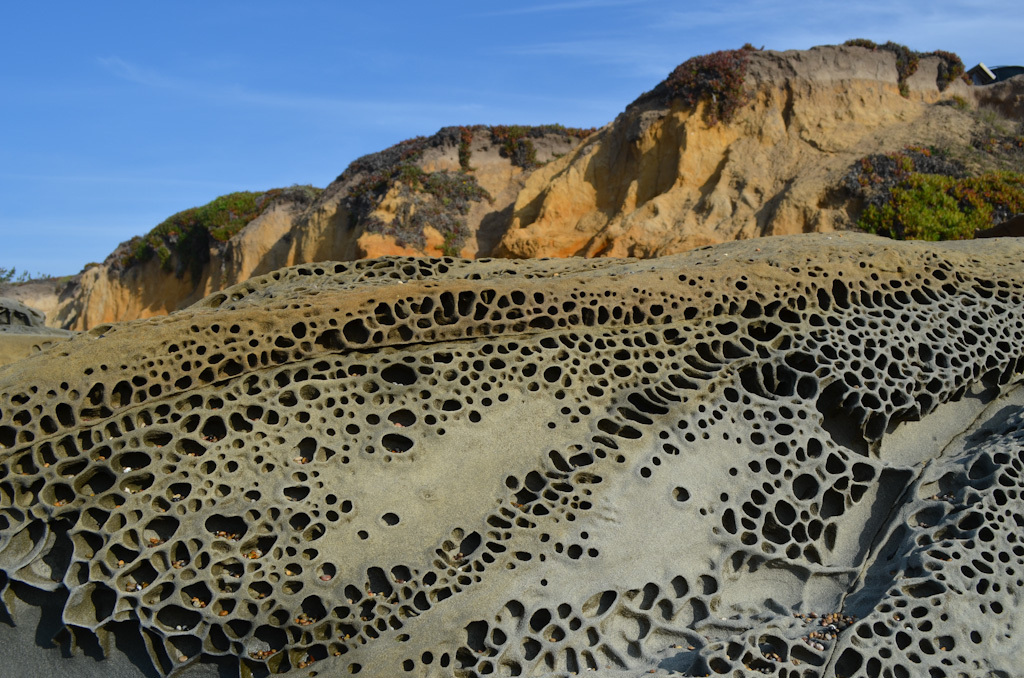
amazing weathering
Starter: Try to explain what has happened in each of the pictures above. What has caused these features (apart from the sheep) to occur?
Weathering & Landscapes
Starter: Take a close look at the three images above. What has happened? The answer is weathering but what makes this different from erosion? Weathering happens to rock that is in-situ and so is not the same as what happens in rivers and oceans where material is on the move.
Make a copy of this definition:
Weathering is the break-up and decomposition of rocks in-situ (in their place of origin). Weathering does not involve the movement of material and this makes it different to erosion.
Weathering can be broken into either three categories:
Make a copy of this definition:
Weathering is the break-up and decomposition of rocks in-situ (in their place of origin). Weathering does not involve the movement of material and this makes it different to erosion.
Weathering can be broken into either three categories:
- Chemical Weathering: The break down of rocks caused by a change in their chemical make-up.
- Physical or Mechanical Weathering: The break down of rocks caused by physical processes with no change in the rocks chemical make up.
- Biological Weathering: Biological is sometimes included within physical weathering. Biological weathering is when flora and fauna break down the rock e.g. growing roots systems or burrowing animals.
Task 1 - Click here to be taken to an excellent iGCSE revision page on Weathering created by Mr Greenfield. Make your own copy of each of the tables that show the types of the three different processes of weathering. (Chemical weathering - Carbonation & Hydration & Physical Weathering - Freeze Thaw & Exfoliation)
Task 2 - Create a spider diagram / mind map to show the factors that affect the rates (fast or slow) of weathering.
Task 3 - iGCSE Geography Exam Practice
Explain why rates of weathering may be faster in tropical areas compared to temperate areas (4)
Task 4 - Further case study research.
1. Limestone Case Study - Madagascar Stone Forest. Click here for more information and excellent imagery.
2. Uluru (Ayer's Rock), Australia - Click here for more information
Create a revision fact sheet for one of these places with annotated photos and information on which type of weathering was responsible for its creation.
Task 2 - Create a spider diagram / mind map to show the factors that affect the rates (fast or slow) of weathering.
Task 3 - iGCSE Geography Exam Practice
Explain why rates of weathering may be faster in tropical areas compared to temperate areas (4)
Task 4 - Further case study research.
1. Limestone Case Study - Madagascar Stone Forest. Click here for more information and excellent imagery.
2. Uluru (Ayer's Rock), Australia - Click here for more information
Create a revision fact sheet for one of these places with annotated photos and information on which type of weathering was responsible for its creation.
Knowledge Stop Check - Got it?
Click here to be taken to the GCSE revision page for this section.