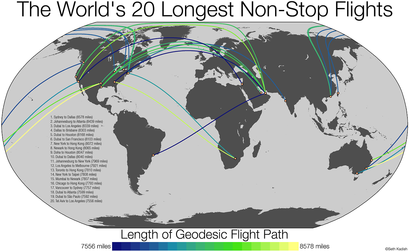
To Start With ......
Reduction in the
Objective: To be able to explain how a reduction in the friction of distance results in time–space convergence.
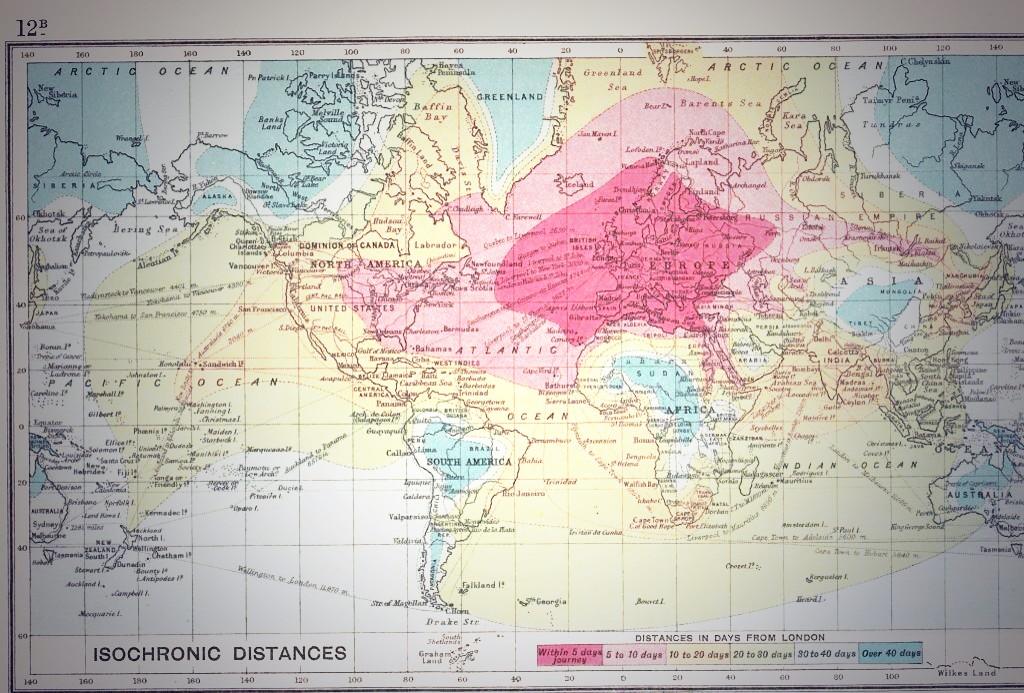
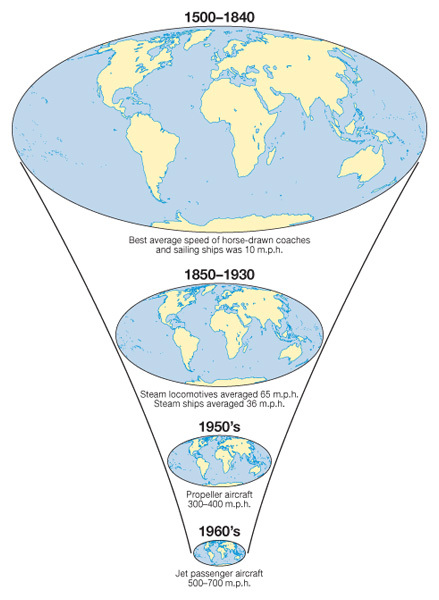
Friction of Distance: This is the reduced likelihood of people using a service the greater the distance that they live from it. Distance is an issue due to the time and costs to overcome it. e.g. reduction in commuting to IST with increasing distance from Colomiers. Friction of distance is closely related to transportation and accessibility. Time-Space Convergence: This is when travel time between places decreases and distance declines in terms of its significance. It is generally brought about by transport innovations and improvements e.g. Airbus A380 can fly Paris to Adelaide in just 20 hours in 2013. (see first image on the right) Starter: Watch the first video to the right and study the Google Map showing location of filming here. Explain the relationship between Idiot Abroad Series 2 and the reduction of friction of distance and resultant time space convergence. Turn to page 27 in the Global Interactions textbook. Task 1. i. Define the following: a. Transport Systems b. Communication Sytems ii How has television been responsible for the diffusion of new ideas around the world? iii Click on the map on the right to enlarge. How is what is shown an example of a transport revolution? Turn to page 28 iv - Study figure 1 and pull out the 10 most important transport and communications milestones that have had a direct effect on the reduction of friction of distance. Task 2
a. Watch the video (IB Geography Globalization) to the right. Make notes on each of the factors that James May claims to have "made the world a smaller place". b. Which factor do you think has been the most influential in shrinking our planet? |
|
Containerization
|
|
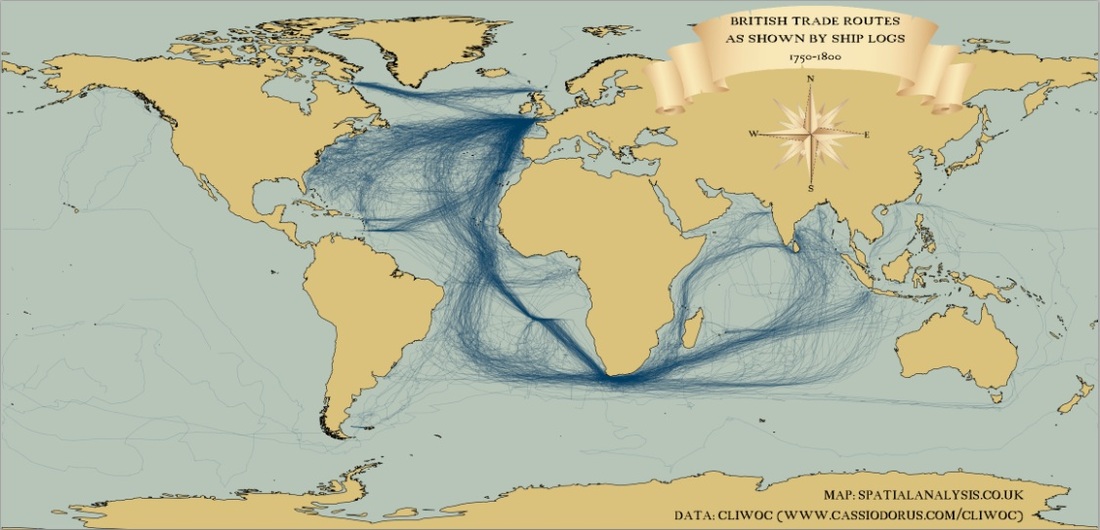
shipping routes 1750 - 1800
Source: http://cdn1.billjaquette.net
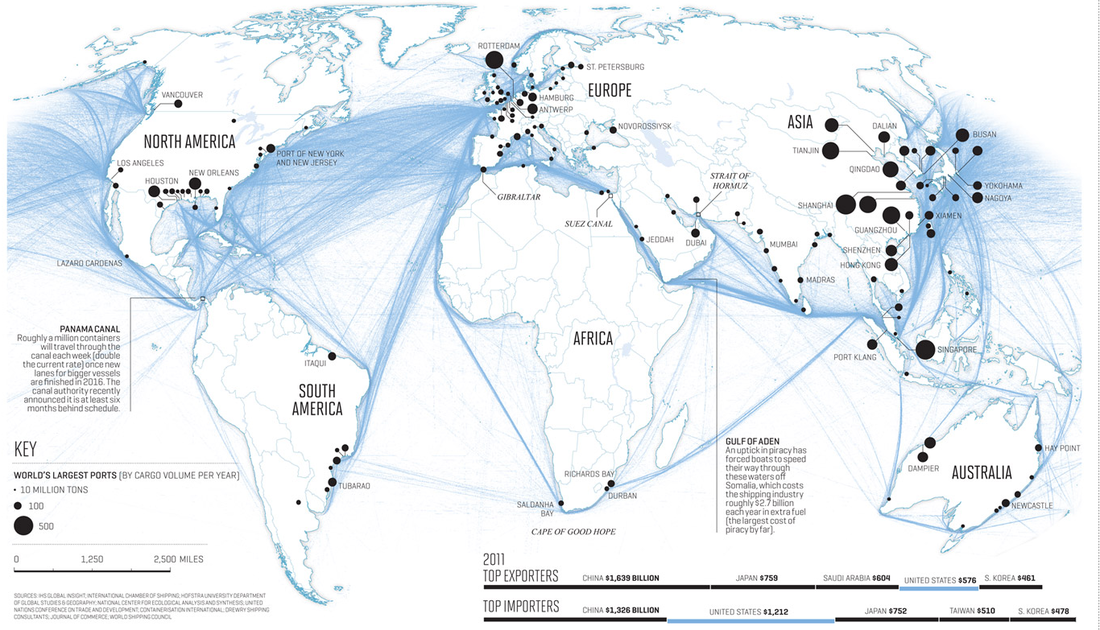
shipping routes modern day
Exam Practice: Use the essay planning tool to help you to complete the following 10 mark question:
Describe and explain the changes in speed and capacity of one type of transport (choose either aeroplane or container ship). (10)
Describe and explain the changes in speed and capacity of one type of transport (choose either aeroplane or container ship). (10)
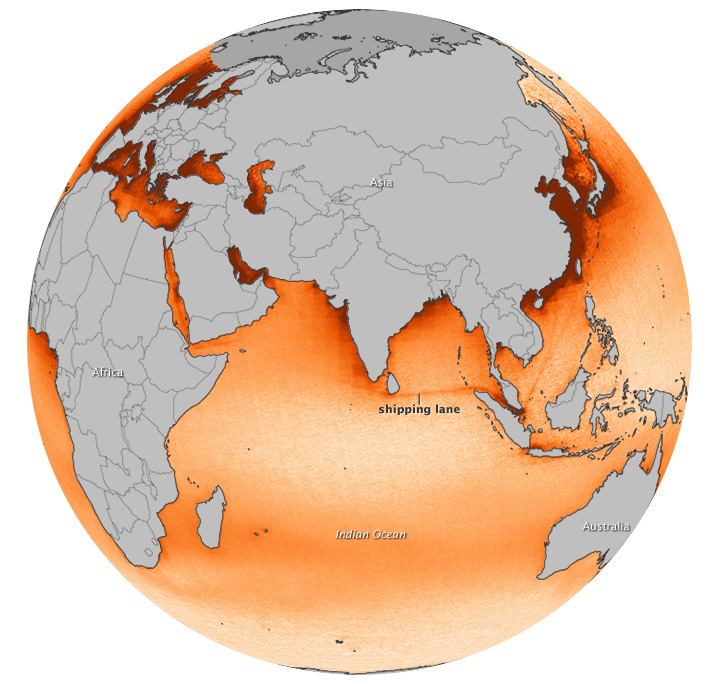
Tracks of elevated nitrogen dioxide levels along certain shipping routes
Internet AdvancesObjective: To be able to examine the changes in the internet, in terms of the extension of links and nodes and the intensity of use at a national or global scale.'
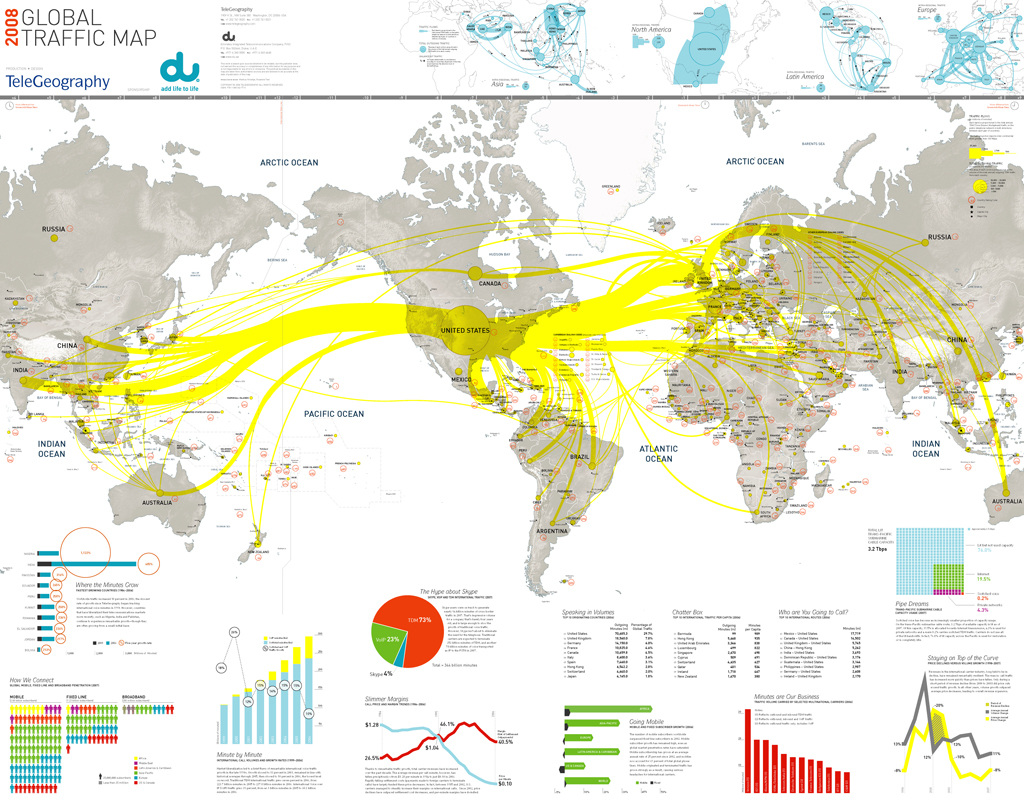
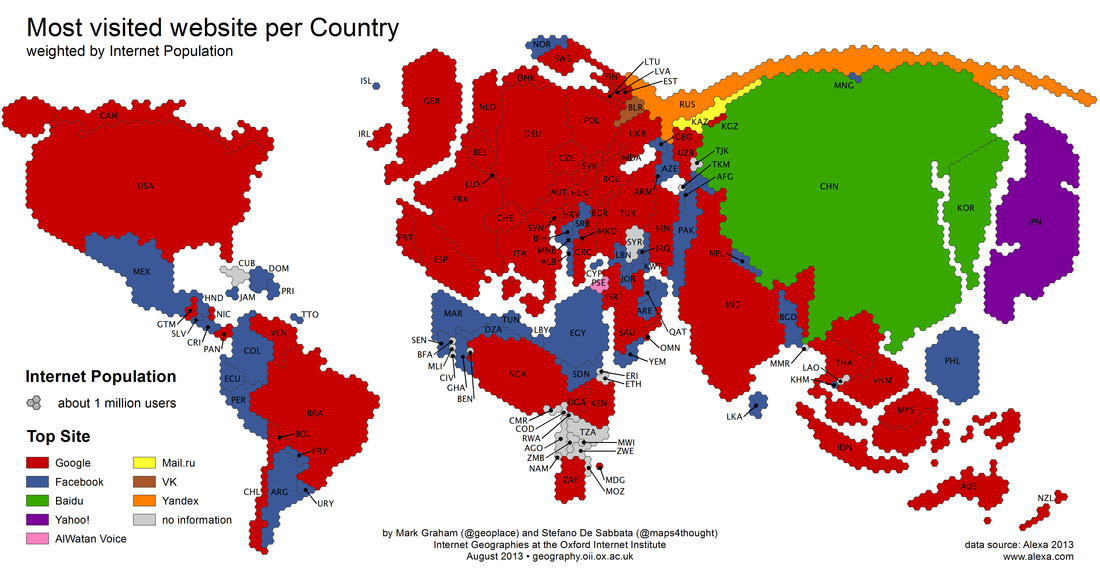
Starter - Check out TWEETPING! - Set this going at the beginning of this piece of work. Let it run for one hour in a new window. Then take a screen shot and comment on the global distribution of tweets making reference to total number and breakdown by continent. To what extent does Twitter reflect the core, semi periphery and periphery model? Task 1 - What is the Internet and how has it developed? Watch the first video to the right hand side and make notes on the key dates and developments up to present day. Then watch the second video and make notes on key social media trends. Task 2 - Study the diagram underneath carefully. i. Click on this link and read through the article carefully.
ii. How is the internet physically connected from country to country and how is the connection carried out? Watch the video to the right. Did you realise that this was the case? Links and Intensity You may well be asked to describe and explain maps that show internet and mobile connectivity. When describing follow the general rules of looking for trends i.e. a high amount of traffic between the US and Europe, looking for anomalies i.e. hardly any internet traffic into Africa and always using figures and the correct units. To help explain why some areas are not connected look at the information below the next table. Below are some reasons to explain traffic between countries and regions. Migration: There is going to be greater flows of traffic between countries that have experienced migration flows e.g. El Salvador and US Colinisation: There are likely to be flows between ex-colonies and colonial powers, especially if there has been migration between the two. Economic and TNCs: There will be strong flows between countries that have economic links. This might be because of the location of TNCs or that they are in trading blocs. Language: Countries with a shared language e.g. English between US and UK are likely to see bigger flows. Offers: There maybe a temporary or permanent increase in traffic if a phone company is offering a special rate between countries. Population size: There is obviously going to be greater flows of traffic between countries with large populations. Wealth: There will probably be stronger flows between wealthier countries because they can afford to establish networks and pay for the services. Education: More educated countries will probably have stronger flows because they understand the technology and can pay for it. |
Task 3 - Study the map above, click on it to enlarge and copy into a Word document.
So, bearing the text (to the left) in mind, describe the links and nodes that exist and the intensity of use at a global scale Additional Reading. i. Read and print out the following articles and summarise what has happened and link to internet usage. a. Excellent article about the recent use of Social Networking and the Arab uprising. b. Excellent October 2012 article about broadband uptake in Tanzania |
Silicon Valley V's Silicon Savannah
Starter: Watch the Ted Talks video below. Make notes on the uptake of mobile phone technology in Africa and how the core & periphery concept is questioned by the speaker.
|
Objective: To examine the levels of uptake in mobile phone technology in the USA and Kenya.
Starter: Watch the BBC link video (blue tab above right) and the embedded Global Digital Statshot to the right. Make notes of the key mobile phone and app usage data as of August 2015. Then watch this taking notes on key concepts. Task 1 - Using the second embedded presentation to the right, take the key figures for North America and Africa for general mobile phone usage and record them. Task 2 - Watch the 'Spotlight on Africa' YouTube video below right and make notes on the story of mobile use in Africa, including the key economic data. Then study this 2016 report from the Financial Times outlining the development of mobile technologies in Africa. Task 3
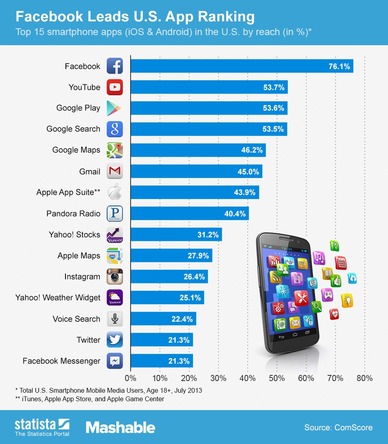
Study the graph above carefully (France is there for reference to our home country). i. Why is there no phone usage before 1988? ii. Describe the differences in the level of uptake in all three countries since 1988. Case Study - Kenya Task 4 - Annotate on to your iPhone worksheet the different ways that the uptake of mobile phone technology effects local populations in Kenya. Your starting point is the embedded SlideShare presentation to the right (slides 1 - 26). Resource 1 - iCow App - Video Resource 2 - Mobile Phone Uptake in Kenya Resource 3 - Apps in Kenya Click here & Most Popular Blackberry Apps in Kenya (thanks Muir!) Task 5 - Click here to read about popular apps for the mobile phone in Kenya. Summarise how Kenyans use their phones. Also, watch the video at the bottom of this page in the 'optional task'. Task 6 - Look at the most popular Android Apps in the USA in 2012 graph. Summarise how USA mobile phone subscribers use their phones and make a comparison to those users in Kenya. Task 7 - Exam Essay "Mobile phone ownership has exploded globally but do display core and periphery characteristics" Discuss to what extent you agree with this statement with reference to two case study countries. (10) Essay Plan framework can be found here Optional Additional Research - Watch the 10 minute documentary beneath taking notes on the uptake or mobile phone usage in Kenya. |
|